Various ways by which P. falciparum parasite evades the immune system via secreted extracellular vesicles
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
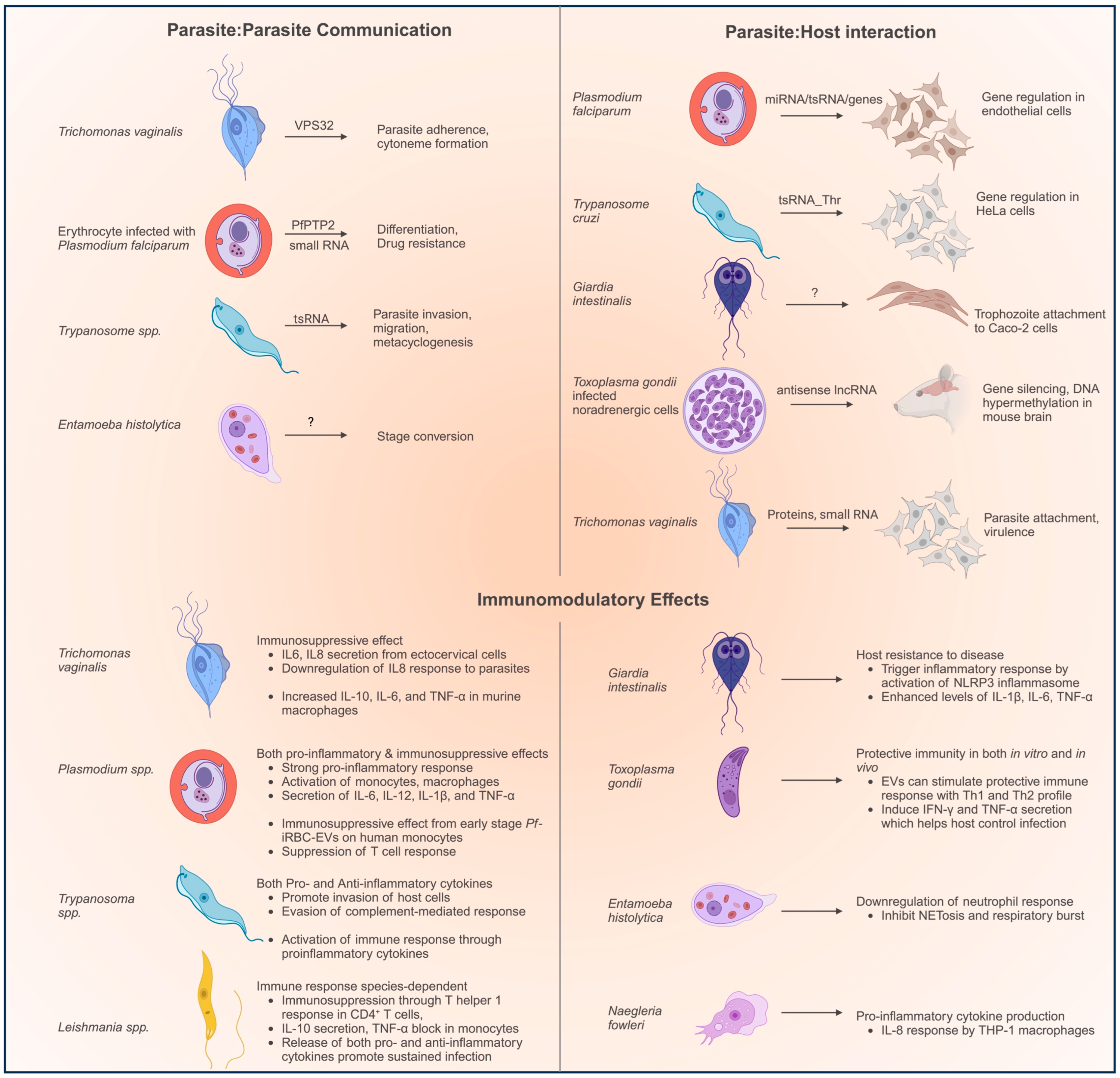
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) secreted by infected red blood cells (iRBCs), as well as other host cells, are important regulators of the balance that determines the disease outcome. In addition, EVs constitute a robust mode of cell-to-cell communication by transferring signaling cargoes between parasites, and between parasites and host, without requiring cellular contact. The transfer of membrane and cytosolic proteins, lipids, DNA, and RNA through EVs not only modulate the immune response, it also mediates cellular communication between parasites to synchronize the transmission stage. Here, we review the recent progress in understanding EV roles during malaria.
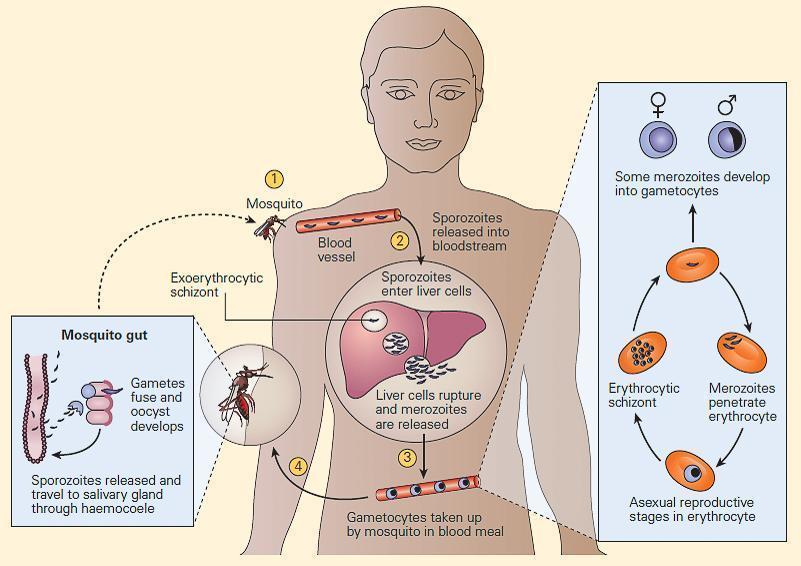
4. Immunity to Malaria
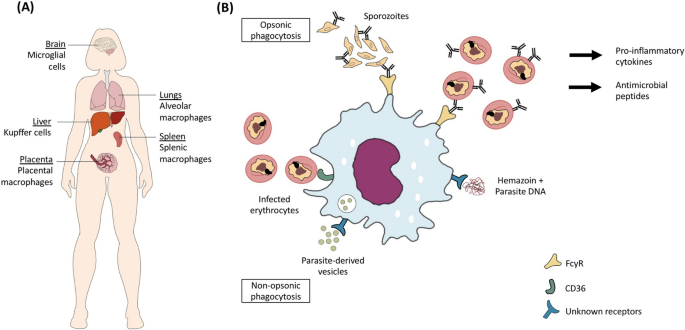
Factors influencing phagocytosis of malaria parasites: the story
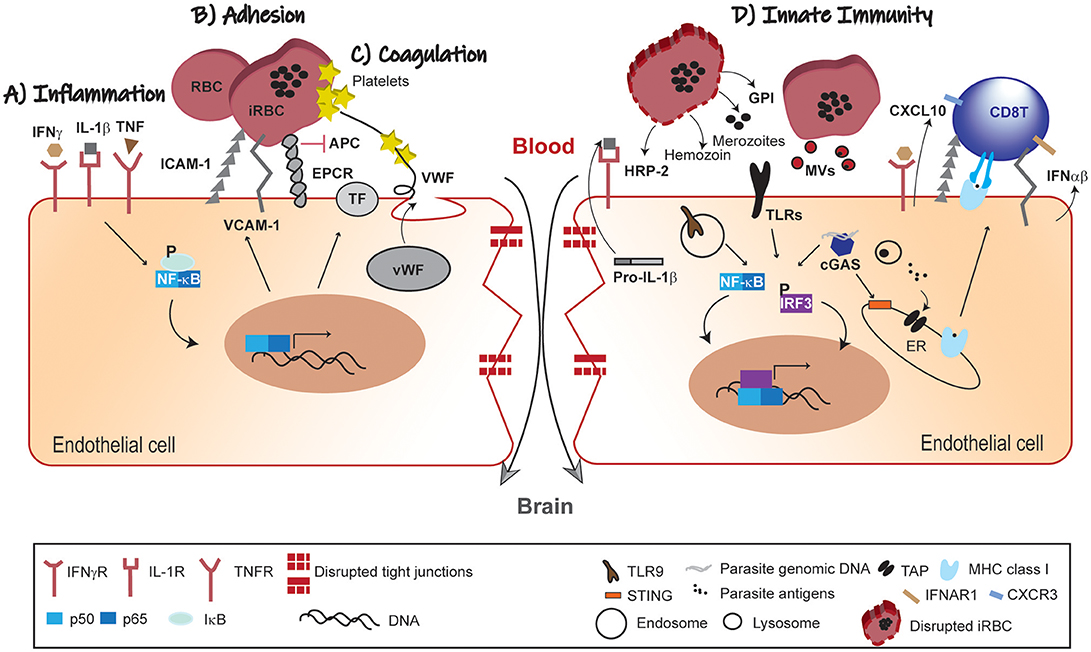
Frontiers Brain Endothelium: The “Innate Immunity Response

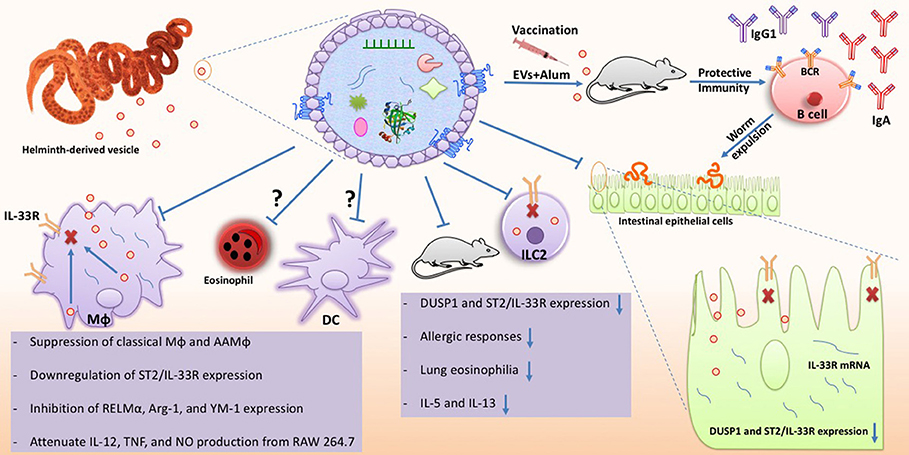
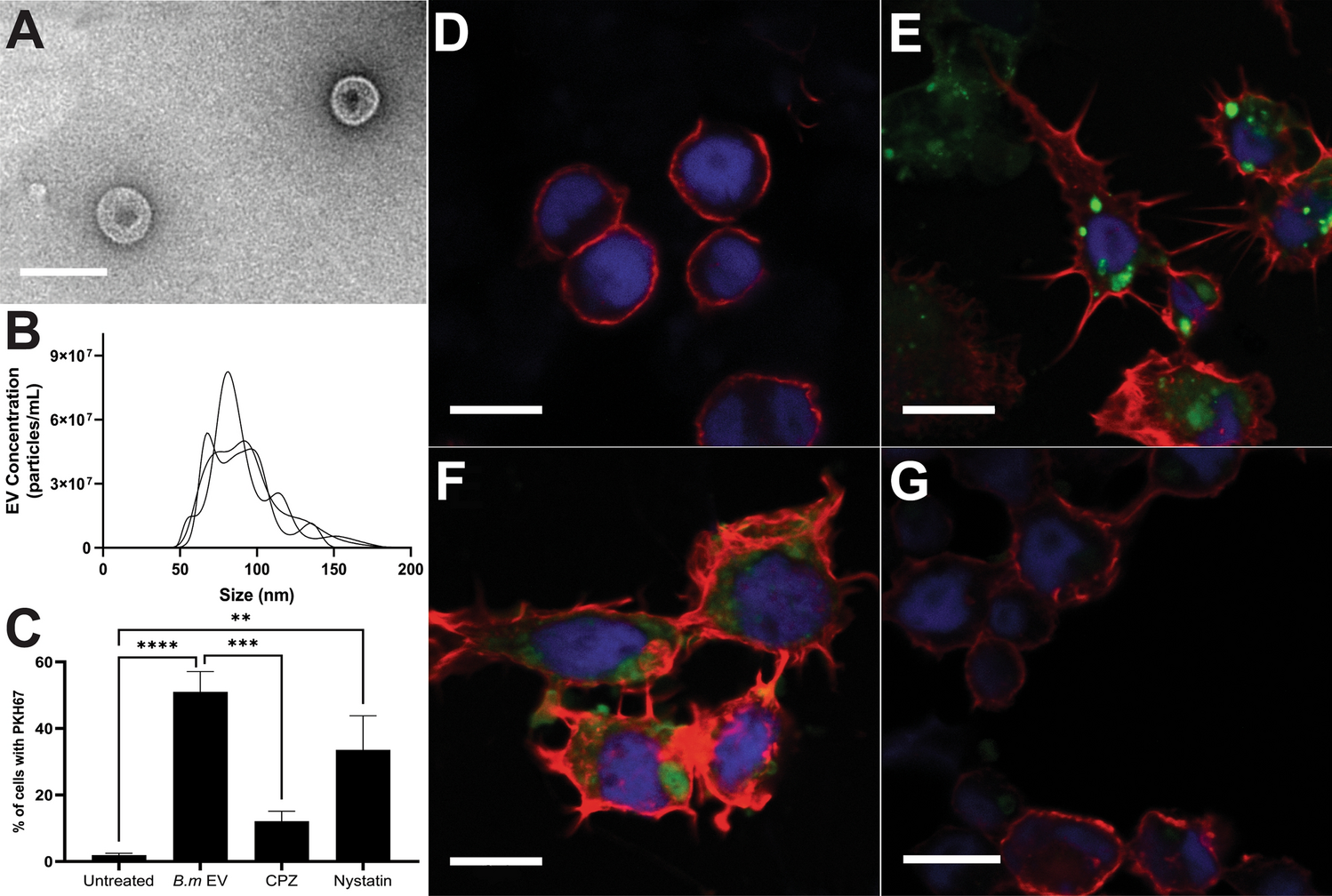
Extracellular vesicles secreted by Brugia malayi microfilariae
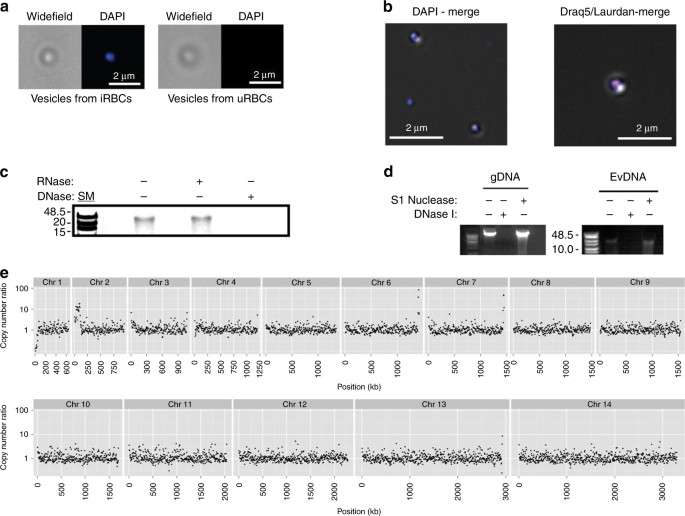
Malaria parasite DNA-harbouring vesicles activate cytosolic immune
TropicalMed, Free Full-Text
Frontiers Immunomodulation by Helminths: Intracellular Pathways

Kinetics measurement of Plasmodium falciparum (Pf)-extracellular
Extracellular vesicles secreted by Brugia malayi microfilariae
Frontiers The Cellular and Molecular Interaction Between
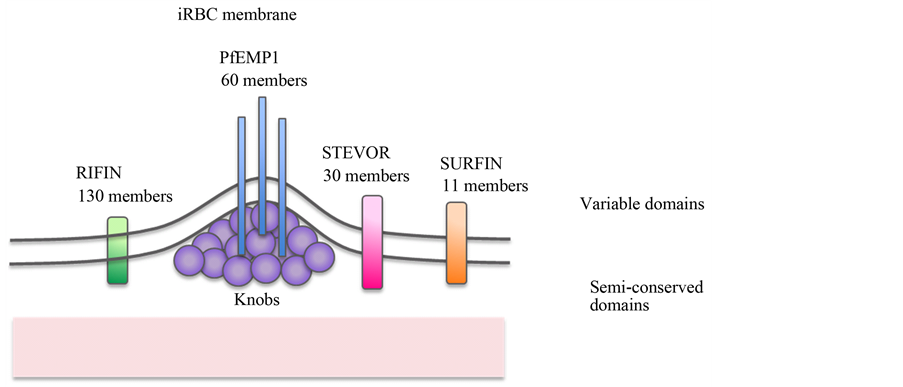
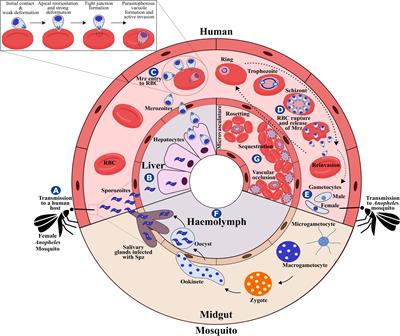
Immune evasion by Plasmodium falciparum parasites: converting a

Extracellular vesicles isolated from P. falciparum carry RNA. (a

The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Immunomodulation and
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







