Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Beyond their role in hemostasis, platelets have emerged as key contributors in the immune response; accordingly, the occurrence of thrombocytopenia during sepsis/septic shock is a well-known risk factor of mortality and a marker of disease severity. Recently, some studies elucidated that the response of platelets to infections goes beyond a simple fall in platelets count; indeed, sepsis-induced thrombocytopenia can be associated with—or even anticipated by—several changes, including an altered morphological pattern, receptor expression and aggregation. Of note, alterations in platelet function and morphology can occur even with a normal platelet count and can modify, depending on the nature of the pathogen, the pattern of host response and the severity of the infection. The purpose of this review is to give an overview on the pathophysiological interaction between platelets and pathogens, as well as the clinical consequences of platelet dysregulation. Furthermore, we try to clarify how understanding the nature of platelet dysregulation may help to optimize the therapeutic approach.
Cells, Free Full-Text

Cell-Free Translation Systems
Biology, Free Full-Text

Circulating Tumor Cells, Disease Progression, and Survival in Metastatic Breast Cancer

Postbiotics-parabiotics: the new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods, Microbial Cell Factories

PDF) Comparative separation methods and biological characteristics of human placental and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in serum-free culture conditions

Label-free, full-field visualization of red blood cell (RBC)
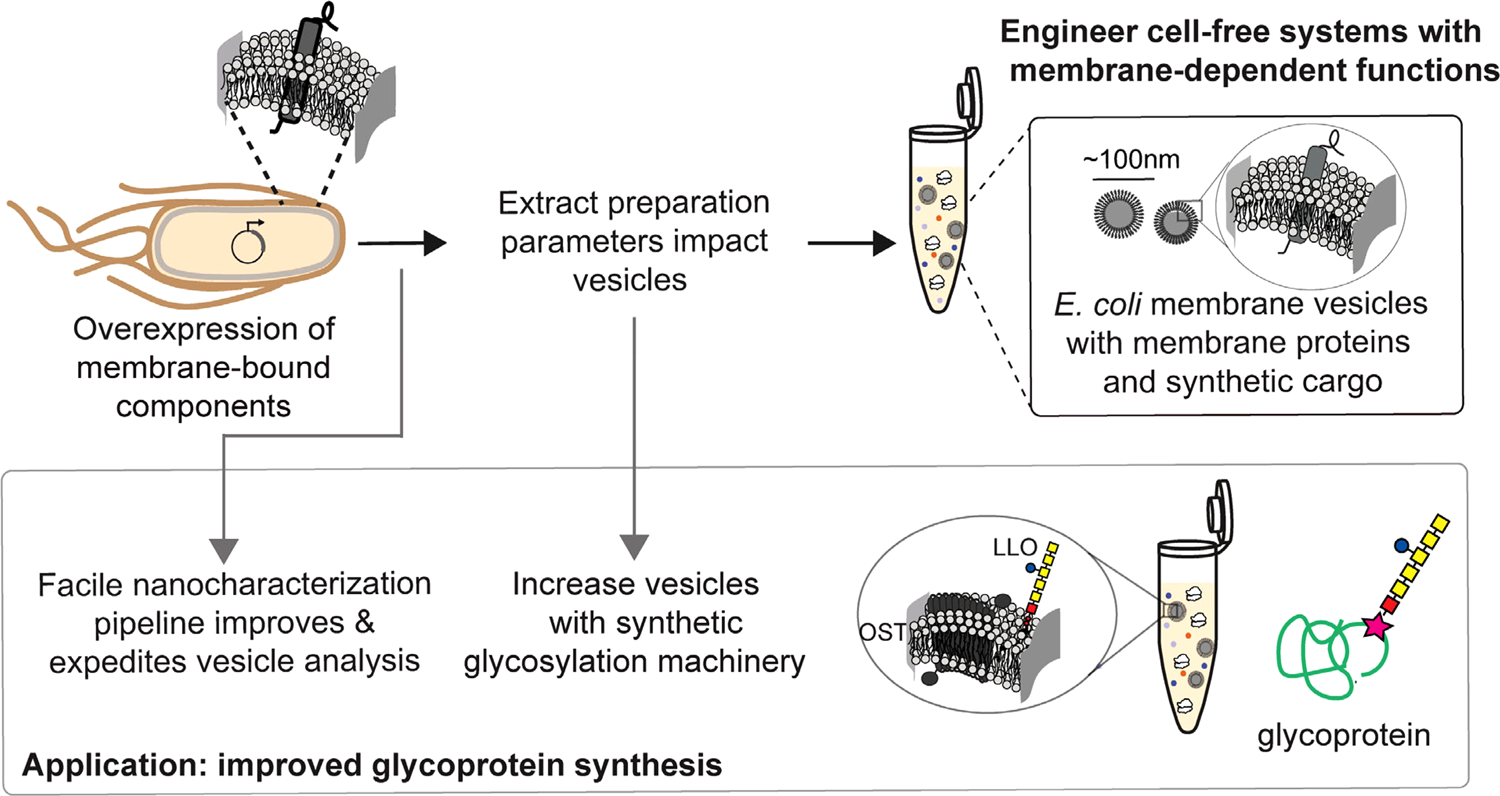
Improving cell-free glycoprotein synthesis by characterizing and enriching native membrane vesicles
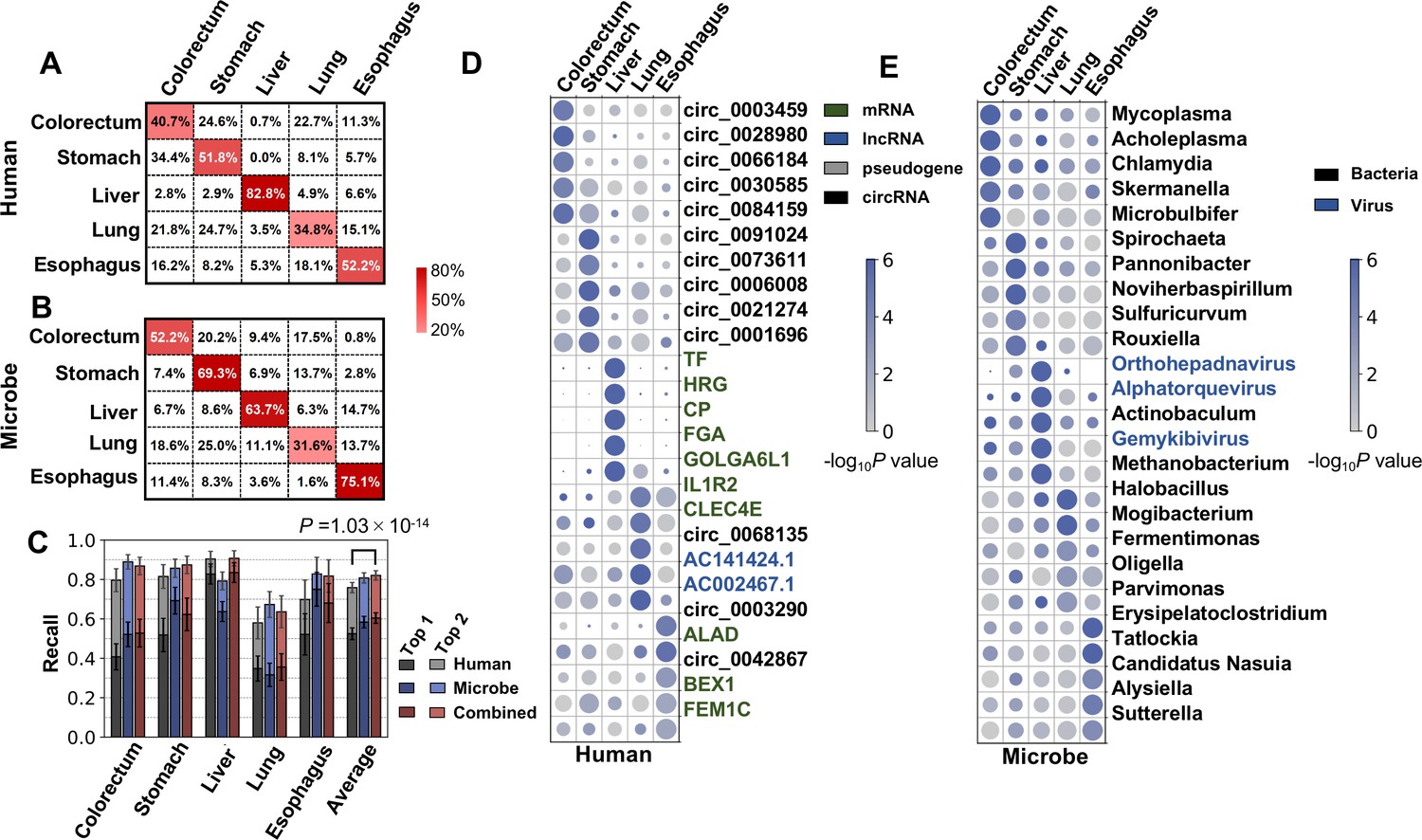
Cancer type classification using plasma cell-free RNAs derived from human and microbes
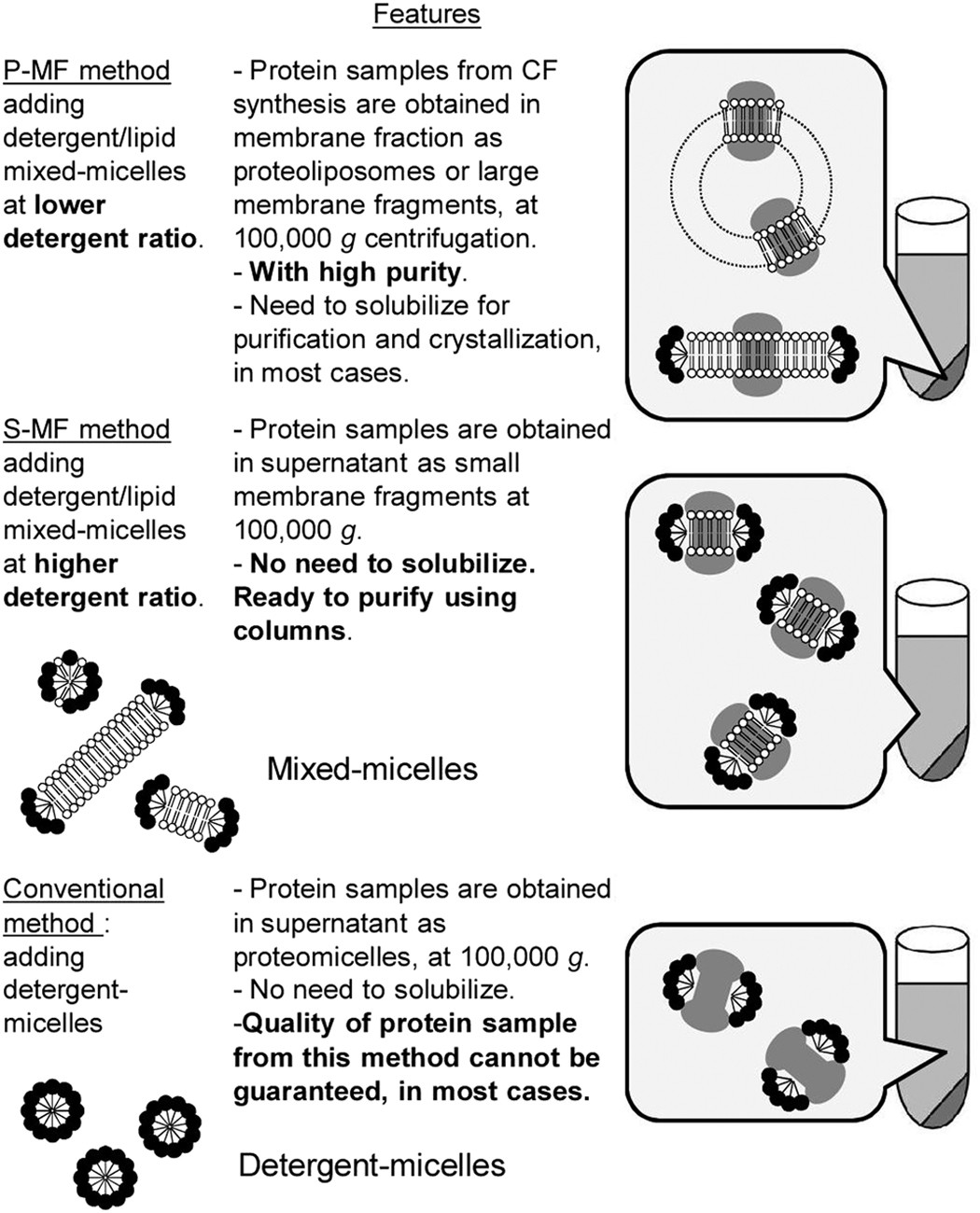
Cell-free methods to produce structurally intact mammalian membrane proteins
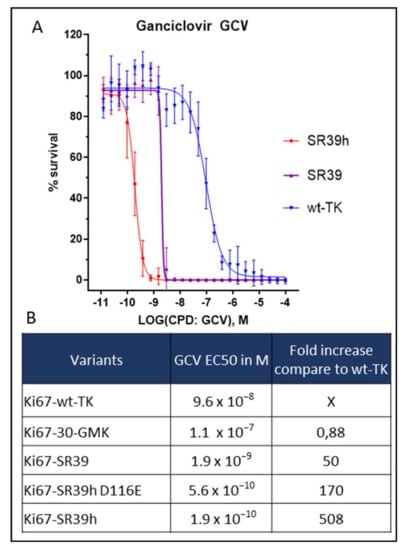
Serial Number Alcohol 120 1.9 6 - Colaboratory

Effect of calendar ageing on the cycle life of anode-free full-cells.
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)






